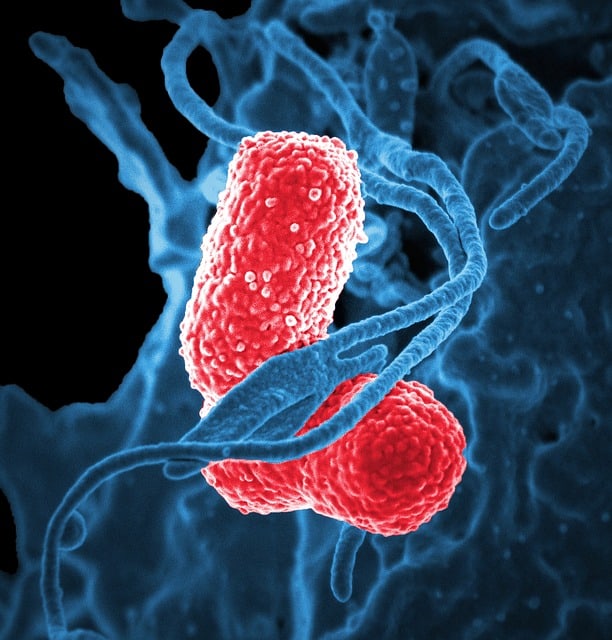
PNEUMONIA is an infection in one or both lungs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. Bacterial pneumonia is the most common type in adults. Pneumonia causes inflammation in the air sacs in your lungs, which are called alveoli. The alveoli are filled with fluid and pus making it difficult for one to breath.
Pneumonia symptoms can be mild to life threatening. The most common symptoms of pneumonia can include coughing, that may produce phlegm, fever, sweating and chills. Individuals with pneumonia also show shortness of breath and chest pain. Children under the age of five years may have fast breathing called tachypnea. Infants may vomit, experience lack of energy or have trouble drinking or eating.
Pneumonia’s classification is three folds based on the germ causing pneumonia, the location in which it was acquired and how it was acquired.
Bacterial pneumonia is by far the most common and is caused by streptococcus pneumoniae. Chlamydophila and Legionella can also cause bacterial pneumonia. Viral pneumonia often causes pneumonia especially in young children and elderly people. Viral pneumonia is often self-limiting and last for a short duration. Mycoplasma pneumonia is caused by mycoplasmas which are neither bacterial nor viral but have traits common to both and this type is often mild in presentation. Fungal pneumonia is often caused by fungi from soil or bird droppings.
Fungal type of pneumonia is common in people with chronic diseases or weakened immune systems. Classification based on where it was acquired is either Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) or nosocomial pneumonia referring to pneumonia contracted by a patient in a hospital at least 48 to 72 hours after being admitted in hospital.
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) refers to pneumonia that is acquired outside of a hospital or institutional setting. Aspiration pneumonia occurs when you inhale bacteria into your lungs from food, drink or saliva. This type of pneumonia occurs in individuals with swallowing problems or due to a sedating effect of medication, alcohol or illicit drugs. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) is commonly seen in high care or Intensive Care Unit (ICU).
Anyone can get pneumonia, but certain people are at high risk.
Infants from birth to two years and individuals over the age of 65 years are susceptible to pneumonia infections.
People who have had a stroke, swallowing problems and those that are bed ridden and have weakened immune systems have also high risk of contracting pneumonia.
Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs are used to treat pneumonia.
Dr. Makemba Shayela Nelson – MBChB – University of Kwazulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, Nesha Medical Practice.
Source: Confidente